Accelerate your infectious disease research with in-depth genomic profiling
Comprehensive genetic information provided by Single Molecule, Real-Time (SMRT) sequencing has radically increased our understanding of microbial genomics, pathogenicity, and antimicrobial resistance. The PacBio systems empower scientists to:
- Generate closed microbial genomes and plasmids to uncover the drivers of pathogenicity, virulence, and drug resistance
- Resolve viral populations to unravel host pathogen dynamics and advance the design and evaluation of drugs and vaccines
- Characterize microbial populations to understand how the microbiome impacts human health
Learn how other scientists have used SMRT sequencing to advance infectious disease research:
- Unraveling malaria mysteries with long-read sequencing
- Egyptian Rousette bat genome provides clues to antiviral mystery
- Data release: Zika-susceptible Aedes aegypti de novo genome assembly
- Sequencing 101: Why are long reads important for studying viral genomes?
- Full-length HIV sequences reveal distinction between viruses in brain, other tissue
On-demand webinar series
Learn how scientists are using highly accurate long-read sequencing to make new discoveries about bacteria, viruses, and the complex systems they inhabit and influence.
Blog
Meeting the threat of antimicrobial resistance with HiFi sequencing and artificial intelligence
After conducting a battery of technology comparisons, OpGen’s Ares Genetics has adopted PacBio HiFi microbial whole genome sequencing. The company believes the read length and high accuracy of HiFi data will enable it to develop a suite of cutting-edge AI solutions with potential to revolutionize the way we combat the spread of antimicrobial resistance.
Blog
PacBio-Powered Analysis Indicates Methylation Makes TB Pathogen So Wily
Scientists have long struggled to explain the success of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the face of effective therapeutics. Tuberculosis (TB) kills more than 1 million people annually, and has a remarkable ability to develop resistance to drugs despite its stable genome. But now, a study from researchers at San Diego State University and other institutions strongly suggests that methylation rather than genome sequence gives M. tuberculosis its broad phenotypic range.
Spotlight
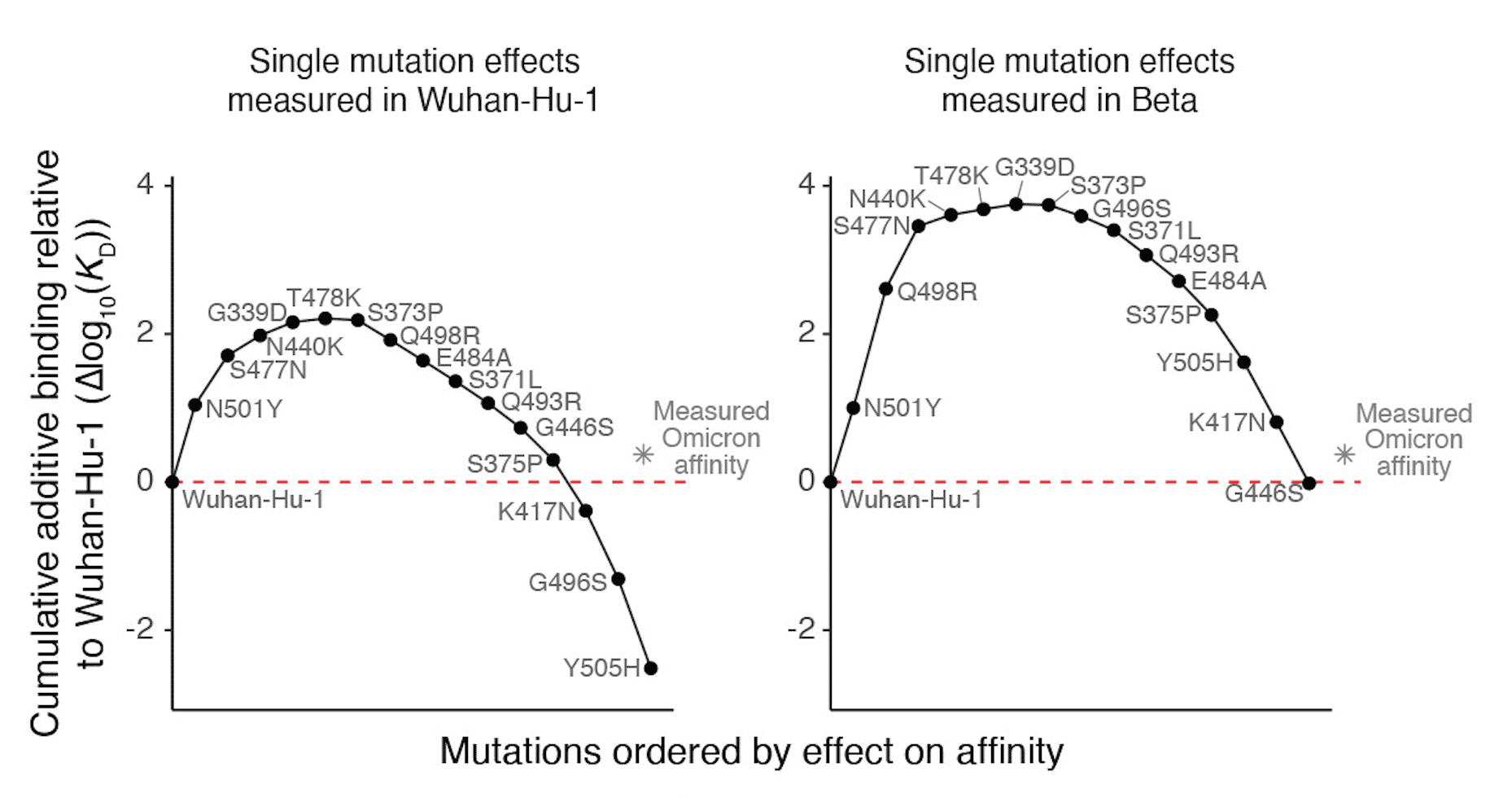
VIRAL EVOLUTION: ASSAYING HOW THE PAST SHAPES THE FUTURE
SARS-CoV-2 mutations in the spike receptor binding domain (RBD) not only directly impact ACE2 receptor affinity but may also modulate the impact of future mutations. Here, a HiFi screening assay is used to measure how individual RBD mutations present in widely circulating variants affect the ACE2 binding affinity of all possible subsequent single amino-acid mutations.
Starr, et. al. (2022) Shifting mutational constraints in the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain during viral evolution. Science.
Spotlight
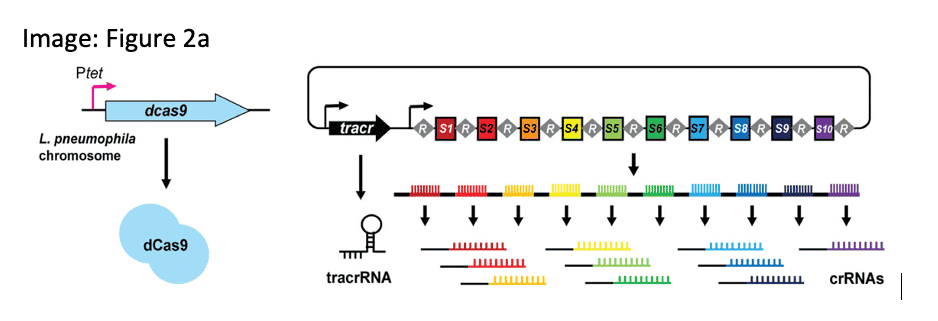
DECONVOLUTING COMPLEX VIRULENCE GENE SYSTEMS
The deletion of individual virulence genes from L. pneumophila genomes that contain a wealth of such genes does not yield growth phenotypes, making it difficult to connect effector genotype to phenotype. To deconvolute redundancy and synergy in this gene family, the authors developed a HiFi sequencing assay for titratable, multiplex gene knockdown.
Ellis, N.A. (2021) A multiplex CRISPR interference tool for virulence gene interrogation in Legionella pneumophila. Communications Biol.