Epigenetics with long-read sequencing
The unique chemistry of long-read HiFi sequencing technology enables researchers to directly reveal the epigenetic landscape of samples. On-instrument 5-base HiFi sequencing detects 5mC methylation in standard sequencing runs without any changes to library prep or sequencing workflows required.
HiFi sequencing provides accurate DNA base calls and simultaneous 5mC detection in CpG context without any additional library preparation. This feature enables the resolution of methylation profiles with phased haplotyping. Human genome researchers may also use this capability to interrogate imprinting disorders and methylation abnormalities associated with tandem repeats.

Application Brief
MEASURING DNA METHYLATION WITH 5-BASE HIFI SEQUENCING
Genome-wide detection and phasing of genetic and epigenetic variants from a single library prep. HiFi sequencing of a single sample detects methylation patterns across the genome, such as hypomethylation at transcription start sites. Sequencing multiple samples identifies differential methylation.
EPIGENETIC SEQUENCING - HOW PACBIO COMPARES
EPIGENETIC ANALYSIS WITH 5-BASE HIFI SEQUENCING
PacBio HiFi sequencing simultaneously calls the four DNA bases and 5mC from untreated genomic DNA. Achieve genome-wide detection and phasing of genetic and epigenetic variants from a single, standard HiFi library prep with long and accurate reads.
With the power of long-read sequencing, you can achieve:
Epigenetics in every run — no bisulfite treatment required
Unlike methods that require chemical conversion of DNA, HiFi sequencing detects modifications in native DNA through impacts on the kinetics of base incorporation.
High accuracy of sequence and methylation
Methylation detection with HiFi sequencing is highly concordant to bisulfite sequencing.
Access the full genome
Access difficult regions of the genome like repeats and centromeres that are beyond the reach of short-read sequencing.
Phasing
Identify allele-specific methylation, whether due to parental imprinting, genetic variation, or repeat expansions.
In the example shown below, a repeat expansion on one allele can be seen to impact adjacent methylation status.
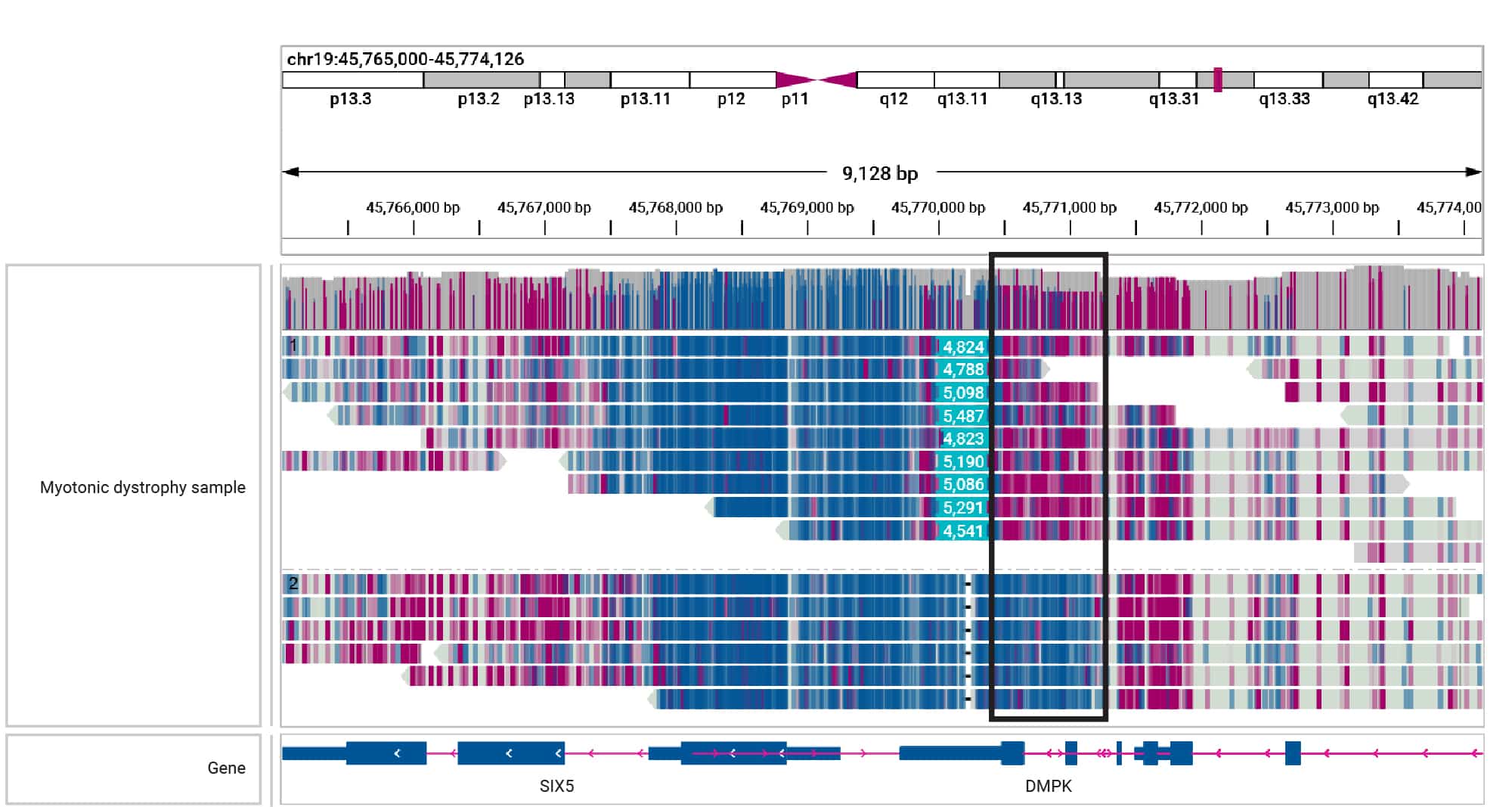
Figure 7. HiFi sequencing phases and identifies hypermethylation of the region adjacent to a mosaic 5 kb DMPK expansion in a sample with myotonic dystrophy (Children’s Mercy Kansas City). Magenta indicates methylation, while blue indicates unmethylated bases.
“SMRT sequencing is opening up new diagnostic avenues, such as the ability to determine tandem repeat lengths, interruptions, and even epigenetics in a single test at base pair resolution.”1
– Ardui, et al., 20181
Epigenetic analysis in action
pb-CpG-tools
The pb-CpG-tools collection provides tools for secondary analysis of CpG methylation data from PacBio HiFi reads. Starting from a pileup of HiFi reads with methylation tags, the tools calculate the percent of reads methylated at every CpG site in the genome.

Direct detection of DNA methylation
See how scientists use PacBio sequencing to detect methylation with basepair resolution.
Genome-wide detection of cytosine methylation
Read how researchers use the kinetics in HiFi reads to determine methylation status at CpG sites.

DNA 5mC detection and methylation phasing
Read how circular consensus sequencing enables genome-wide detection of cytosine methylation by single molecule real-time sequencing.
Explore
Did you know we have over 10,000 articles, reports, papers, and videos related to epigenetic research?
APPLICATIONS FOR EPIGENETIC ANALYSIS
What 5-Base Sequencing Reveals
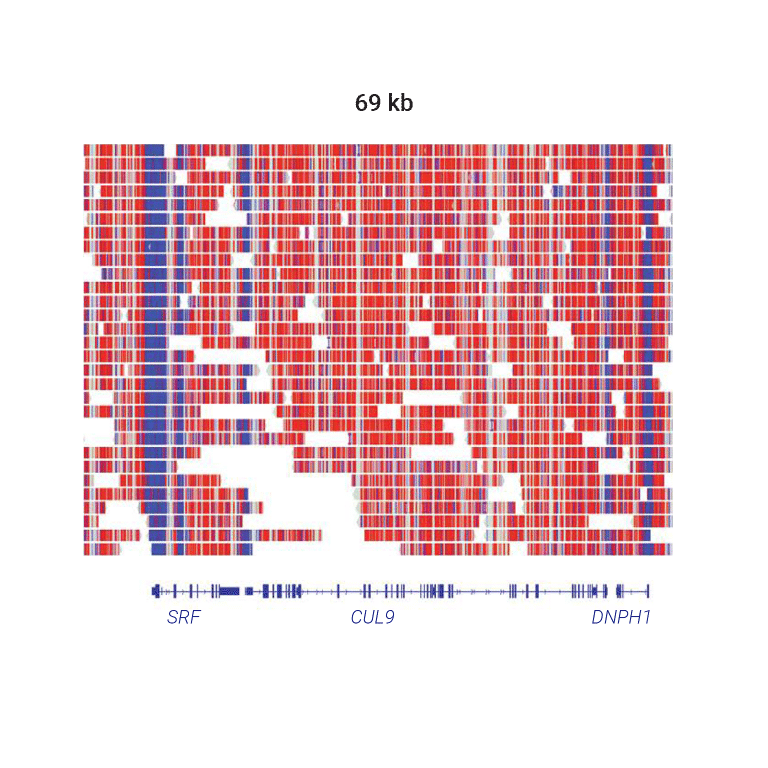
Regional methylation patterns
Methylation levels vary across the genome in many species. In vertebrates like human most CpG sites are methylated. Active gene transcription start sites are often hypomethylated.
In this example genomic region, 5-base HiFi sequencing of the human HG002 sample shows overall hypermethylation (red) with hypomethylation (blue) specifically at transcription start sites.
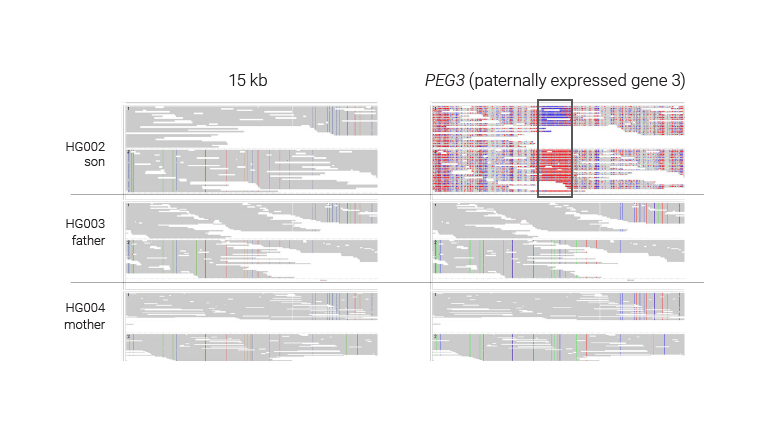
Phased genetics and epigenetics
HiFi sequencing enables simultaneous phasing of reads into maternal and paternal haplotypes and detection of methylation. This reveals allele-specific methylation patterns, which can be due to genetic variation (where epigenetic status is affected by a difference in sequence) or parental imprinting (where epigenetic status is affected by whether a chromosome was inherited from the mother or father).
In this example, the HG002/3/4 trio from Genome in a Bottle, HiFi reads show the expected maternal imprinting at the gene PEG3. HiFi sequencing allows phasing of the haplotypes per sample, the trio identifies which allele is transmitted from which parent, and 5-base sequencing shows allele-specific methylation.
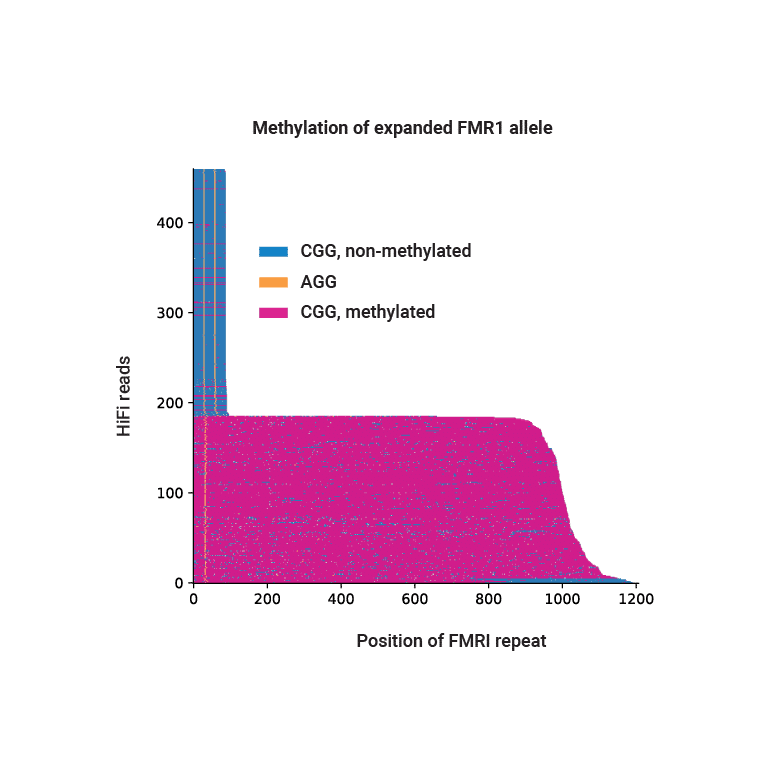
HiFi sequencing phases and identifies hypermethylation of expanded FMR1 repeats in NA07537.
Methylation and disease
Atypical methylation patterns contribute to rare diseases like Prader-Willi syndrome and are important factors in pathogenic repeat expansion, such as the CGG expansion at the FMR1 locus that cause Fragile X syndrome. With high accuracy, long reads, and methylation detection, HiFi sequencing is ideal for characterizing these repeat expansions.
Epigenetic sequencing workflow at a glance
Standard sequencing run
- Simultaneously detect accurate base sequence and accurate epigenetic modifications
Simple Analysis
- Detect microbial base modifications and motifs with the microbial genome analysis application in SMRT Link
- Call 5mC at CpG sites directly from the sequencing instrument or in SMRT Link
- Visualize 5mC annotation directly in IGV
Common questions about PacBio epigenetic sequencing
FEATURED LONG-READ SEQUENCING SYSTEMS
5-base genome sequencing is now possible. With PacBio long-read sequencers you can gain immediate access to the epigenome with no special workflow or data processing steps required.

